 You’ll probably be familiar with the ‘Yin – Yang’ symbol – a circle that is half black and half white, with a black and a white dot in each of the opposing ‘tear drop shaped’ halves.
You’ll probably be familiar with the ‘Yin – Yang’ symbol – a circle that is half black and half white, with a black and a white dot in each of the opposing ‘tear drop shaped’ halves.
So, where does it come from and what does it mean?1
As I understand it, the symbol can be traced back to ancient China and its meaning is utilised in the Eastern Philosophies of Taoism and Confucianism.
The symbol represents the idea that the universe, and what lies within, is governed by duality – sets of two opposing and yet complimentary forces.
These forces are not total opposites – they are relative to each other, two sides of the same coin. They don’t, and can’t, exist on their own. They are inter-related parts of a bigger whole.
Some examples:
- Light and dark
- Alive, and not2
- Masculine and feminine
- Good and bad
- Asleep and awake
- Hot and cold
- Rest and movement
- Front and back
- …and we could keep on going!
Further, the two dots ‘within’ each half represent the idea that everything contains the seed of its opposite.
Given this duality, we are best to learn from both the Yin and the Yang, and their inter-relatedness3.
Context
Why am I writing this post? Well, I feel the need to point out – and open up – what I see as a duality.
Over the years I’ve been very aware of how many (most?) organisations, and their management systems, have dwelt on ‘the individual’:
- ‘Here’s your target’ and ‘Here’s your score’
- ‘Well done, here’s a pat on the back’ or ‘Must try harder’
- ‘Here are your values…and the attitude you must adopt’
- ‘It’s your personal responsibility to succeed and progress’
- ‘Do the right thing!’
- …and on and on
Further, much of the work of Deming, Seddon and other giants of mine has been to help organisations move away from focusing on (and usually ‘judging’) the individual and, instead, to work on the system that the individual is working within.
Some classic quotes fit here:
“95% of the reasons for failure to meet customer expectations are related to the deficiencies in the system rather than the employee…the role of management is to change the process rather than badgering individuals to do better.” (Deming)
“People’s behaviour is a product of the system. It is only by changing the system that we can expect a change in their behaviour.” (Seddon)
“A bad system beats a good person every time.” (Deming)
It’s the system, stupid!” (Seddon)
I strongly agree with the messages within the above quotes (and the accompanying bodies of work). However, I consider that we need to retain a focus on the individual, as well as massively working on the environment in which ’we’ work. But such a focus would be to help the individual rather than judge them.
This isn’t a criticism of Deming, Seddon etc. I expect that they would agree.
Two ‘angles’ interest me in this regard:
‘Individual A’ that comes to believe that, if it’s about ‘the system’, then it’s not really ‘their’ problem…so they’ll sit back and wait for ‘others’ (usually up the hierarchy) to ‘solve’ the system; and conversely
‘Individual B’ that really grasps that it’s about the system; takes a huge responsibility (burden) on their shoulders to ‘move’ the system; and then experiences great stress (and potentially depression) from limited successes.
So I’d like to bring it all back to a duality – the individual and the environment they are in.
The Yin – Our environment:
 I run a 2-day course based around Deming’s theory of profound knowledge. The psychology part includes some powerful considerations in respect of social psychology.
I run a 2-day course based around Deming’s theory of profound knowledge. The psychology part includes some powerful considerations in respect of social psychology.
We discuss three of the classic experiments regarding the power of ‘being in a world of others’ (i.e. our environments):
- Solomon Asch’s 1951 ‘peer pressure’ experiment on an individual’s strong urge to conform (fit in) with those around them, where this power can be stronger than their personal values or basic perceptions.
- Stanley Milgram’s 1963 behavioural study on Obedience to Authority, where people do what they are told to, even where this conflicts with their personal values.
- Philip Zimbardo’s 1972 ‘Stanford Prison’ experiment, where the existence (or not) of power led people to adopt abusive (or submissive) behaviours.
The reason for discussing these (in)famous experiments is to open people’s eyes to the huge power of the environment that people are working (and living) within, and that, if we work on getting our environment(s)4 ‘right’ then great things can happen5….and conversely, if we get it wrong, we end up fighting each other for survival.
However, the environment is only part of the picture. It is made up of individuals within, capable of making choices…
It must be, else why would the system be ‘as it is’…and how could it be changed?
The Yang – Us as individuals:
 A (social) environment is made up of individuals.
A (social) environment is made up of individuals.
Some of the nature of that environment is because of how individuals behave within it. Some of it comes from outside forces.
I think that it’s worth constantly thinking about, and working on, the things that ‘I’ (i.e. the individual) can control…and calmly coping with the things that I cannot.
- I know that there are some huge system constraints as to why the current system(s) work as they do.
- I know that they won’t change overnight, just because I ‘pointed them out’ or even because I (and others) tried to do something about them.
In terms of my role within:
- I can choose to think about and (try to) modify my actions and behaviours
- I can choose to ponder how to go about this
- I can choose to persevere, or to pivot – to try different strategies and tactics as I learn what doesn’t seem to work.
- I can choose my attitude about what is before me, and what to do about it.
Attempting to do this is not easy (it takes much thought and constant practice) but it is worthwhile (with meaning).
As an aside: If you want to know more about achieving meaningful change of a system, then you might want to read about normative change.
On Meaning
 One of the most renowned books written which considers, in part, the subject of attitude is Victor Frankl’s ‘Man’s search for meaning’.
One of the most renowned books written which considers, in part, the subject of attitude is Victor Frankl’s ‘Man’s search for meaning’.
The first half of the book describes his terrible experiences as a prisoner spanning three years across four Nazi concentration camps. To put it mildly, it’s not pleasant BUT it is a hugely important piece of work. At his liberation in 1945 all but one of his close family members had died/ been killed.
He pondered much on what could be learned from his experiences. Who had survived? Who had not? And perhaps why? And, in his writings, he provided us with much to contemplate:
“Everything can be taken from a man but one thing: the last of the human freedoms – to choose one’s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one’s own way.”
But why would we choose one way over another?
“The way in which a man accepts his fate and all the suffering it entails…gives him ample opportunity – even under the most difficult circumstances – to add a deeper meaning to his life.
It may remain brave, dignified and unselfish. Or in the bitter fight for self-preservation he may forget his human dignity and become no more than an animal.
Here lies the chance for a man either to make use of or to forgo the opportunities …that a difficult situation may afford him. And this decides whether he is worthy of his sufferings or not.”
What about trying to ignore our circumstances? Frankl reflects on many who took this approach:
“A man who let himself decline because he could not see any future goal found himself occupied with retrospective thoughts…
…but in robing the present of its reality there lay a certain danger…instead of taking the camp’s difficulties as a test of their inner strength…they preferred to close their eyes and to live in the past.
Life for such people became meaningless.”
And, sadly, Frankl’s experience was that those who came to a point without meaning gave up living soon after.
Thankfully, our lives don’t come even close to that of Frankl’s. This fact makes his reflections even more powerful. If lessons on meaning and attitude apply even in a ‘hell on earth’ then they most certainly apply to our ‘ordinary lives’.
Frankl quotes the philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche in his summing up:
“He who has a why to live for can bear with almost any how” and
“That which does not kill me, makes me stronger.”
In short:
- be clear on meaning (what is your longer-term, valuable-to-society, purpose?)
- work through the constant challenges that you most certainly will encounter on the way
- If you move onwards ‘knowing why’, then you can use this to ‘keep yourself grounded’ on the bumpy journey ahead.
Note: This line of thinking opens a related topic, which I hope to write about in a follow-up post in respect of resilience. It’s all very well ‘telling ourselves’ to be resilient, but some help in being so might be useful.
Back to that duality:
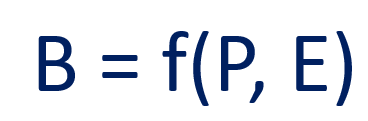 Going back to one of the early social psychologists, Kurt Lewin, we find that he clearly saw the duality. He expressed it as a simple equation:
Going back to one of the early social psychologists, Kurt Lewin, we find that he clearly saw the duality. He expressed it as a simple equation:
‘Behaviour is a function of the person in their environment.’
The equation has two variables: you, and your environment. One doesn’t exist without the other.
Yes, the environment can have a HUGE influence on you and I…but there is a capability within us (the individual) to choose (to a degree) what we think, and do, about it.
Further, within every individual is the seed of their environment influencing them and within every (social) environment there is the seed of the individual able to influence it right back!
Footnotes:
1. Yin and Yang explanation: Here’s a nice short 4 min. animated video that explains at a deeper level: Yin & Yang TED Ed video by John Bellaimey
2. Alive, and not: I’ve deliberately not written ‘life and death’ because the duality is much more than this. There was also a HUGE period of time (circa. 4 billion years) that I wasn’t alive before I was born.
3. Reductionism vs. Synthesis: The underlying message within the Yin and Yang sits very well with Systems Thinking and the truth that reducing a system into its parts will give a limited and limiting view.
4. Environments: We live within multiple, often overlapping, social environments. Our home life, our work life, our communities and our wider society.
5. Deming’s ’14 Points for Management’ are all about creating the right environment for an organisation to thrive.